In essence, fiat money is currency that a government has declared to be legal tender, but it is not backed by a physical commodity. The U.S. dollar is an example of fiat money. Historically, most currencies were based on physical commodities such as gold or silver, but fiat money is not backed by any physical assets.
What is Fiat Money? (Definition #2)
A fiat currency is money that is not backed by any commodity, such as gold or silver. It is just a promise to pay in the future.
Why is Fiat Money Valuable?
Since ancient times, humans have used all sorts of things to trade goods and services. From seashells to salt, just about anything has been used as a form of currency at one time or another. But what makes fiat money so valuable?
Fiat money is valuable because people believe it is valuable. Governments use fiat money to control the economy by controlling how much money is in circulation. And businesses use it to pay employees and suppliers.
History of Fiat Money in the World
The origin of fiat currency can be traced back to the 10th century, when Chinese merchants started using paper receipts as a way to store and trade value. These receipts were known as “jiaozi“, and could be exchanged for goods or services. Over time, the use of jiaozi spread throughout Asia, and eventually evolved into modern-day fiat currency.
In the 11th century, Marco Polo introduced paper money to Europe. The first European paper money was called “banknotes”. It was issued by the Bank of Venice in the 13th century. Fiat money became popular in the 20th century when countries started to issue their own currency.
Fiat money has been used in various forms throughout history, but it wasn’t until the 20th century that it became the predominant form of currency. This was largely due to the rise of central banks and other financial institutions, which helped to stabilize and standardize fiat currency around the world.
History of Fiat Money in the United States
The history of fiat money in the United States can be traced back to the early colonial times. In those days, Spanish silver coins called pieces of eight were used as currency. The coins were minted in Mexico and then brought over to the colonies. They soon became the official currency of the United States.
However, with the growth of the country came the need for a more centralized currency system. In 1792, Congress passed the Coinage Act, which established a Mint and created a national currency. The new currency was based on gold and silver, and consisted of coins such as dimes, quarters, and dollars.
Over time, however, fiat money began to replace gold and silver as the primary form of currency. This was due in part to inflationary pressures caused by wars and other economic crises. By 1933, almost all currencies were fiat money.
Pros and cons of fiat money
Advantages of fiat money include:
- Ease of use and acceptance.
- Can be used to purchase a variety of goods and services.
Disadvantages of fiat money include:
- Susceptibility to inflation.
- Can be devalued by governments.
Learn more: Compound interest can help you overcome the effects of inflation.
(Hyper)inflation due to Fiat Money
Hyperinflation in Venezuela
In recent years, Venezuela has been plagued with high levels of inflation. The root cause of this hyperinflation is the country’s reliance on fiat money. Fiat money is paper currency that is not backed by any physical commodity. This makes it vulnerable to rapid inflation rates when the government prints too much of it.
Venezuela’s hyperinflation has caused immense hardship for its citizens. The prices of basic goods and services have skyrocketed, making it difficult for people to afford even the most basic necessities. Many Venezuelans have had to flee their country in order to find food and shelter elsewhere. The Venezuelan example shows that fiat money can be a very risky form of currency.
> See more examples about Hyperinflation.
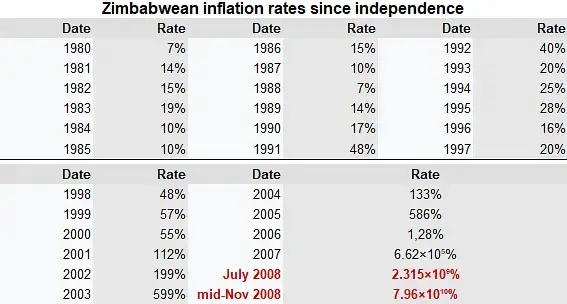
Hyperinflation in Zimbabwe (Example)
To widen a pandemic scourge, Zimbabwe posted a severe case of hyperinflation ten years ago. Its inflation-rate rate for November 2008 reached a staggering 79.6 billion percent (a day-for-day inflation of 98%).
Inflation in Argentina
In the early 21st century, Argentina suffered from high levels of inflation. Many economists believe that this was in part due to the government’s printing of large amounts of fiat money. When a government prints large quantities of fiat money, it can lead to inflation as the increased supply drives down the value of each unit of currency. This was seen in Argentina in the early 2000s, when prices rose rapidly and the value of the peso plummeted.
In Argentina, the government has a habit of printing more money than it has in reserves, which causes inflation. For example, in 2012, the government printed money to pay off its debt, which caused prices to rise by 25%. In 2015, the government did the same thing and prices rose again by 40%.
The future of fiat money
As society becomes more and more digital, it’s no surprise that currencies are following suit. With the advent of Bitcoin and other digital currencies, many are asking whether fiat money has a future. On one hand, fiat money is backed by governments and central banks, which gives it a certain level of trust and stability. Digital currencies, on the other hand, are not backed by anything and can be incredibly volatile.
Another issue with digital currencies is that they can be used for criminal activities such as money laundering or terrorist financing. Fiat money is much more difficult to use for these activities because it can be traced more easily. Despite these disadvantages, there are some advantages to digital currencies. They can be used for faster and cheaper transactions than fiat money. They also offer more privacy than traditional banking systems.
